Image
Objective
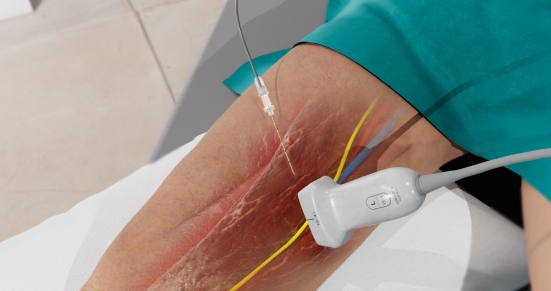
Injection of local anaesthetic lateral to the femoral artery within the adductor canal. The local anaesthetic targets the Saphenous nerve located within the adductor canal at the mid thigh level.
Technique:
- Begin by slightly externally rotating the knee with the patient supine.
- Place the transducer in a transverse orientation midway between the patellar tendon and inguinal crease over the Sartorious Muscle.
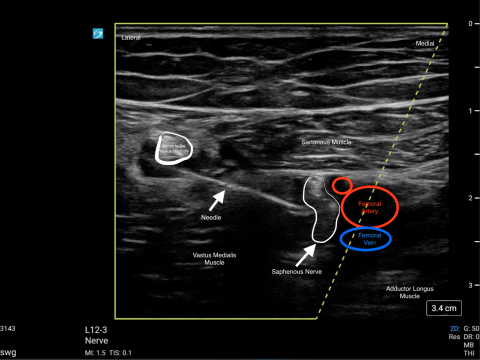
- Identify the Femoral Artery and Vein within the Adductor Canal formed by the Sartorious Muscle (anterior wall), the Vastus Medialis (lateral wall) and the Adductor Longus (medial wall). The Saphenous Nerve is sometimes visualised within the canal.
- Use an in-plane lateral to medial approach with the block needle. The initial injection should occur lateral to the Femoral Artery within the Adductor Canal.
Image
Patient Positioning:
Supine, knee slightly externally rotated
Transducer:
Teaching Points:
- The Adductor Canal Block is a sensory only block targeting the Saphenous Nerve which should allow for early ambulation postoperatively.
- In addition to injection of local anaesthetic lateral to the femoral artery, it may be beneficial to inject local anaesthetic medial to the femoral artery via hydrodissection between the Sartorious muscle and Femoral Artery. This may ensure a more complete consistent block.
- Care should be taken not to perform the Adductor Canal Block too proximal. This may result in a block of the Femoral Nerve if a high volume of local anaesthetic is used.
The Nerve to the Vastus Medialis may be visualised lateral to the Adductor Canal. Care should be used to avoid injury to this nerve with the block needle on approach to the Adductor Canal. You may choose to block this nerve if visualised.
Click to download the guide today.

