S Series: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular Level 1
S Series: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular Level 1

/sites/default/files/201410_Image_S-System_Brachial_Plexus_Supraclavicular_Level_1.jpg
S Series: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular nerve block Level 1.
Clinical Specialties
Media Library Type
Media Library Tag
Body
S Series: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular nerve block Level 1.
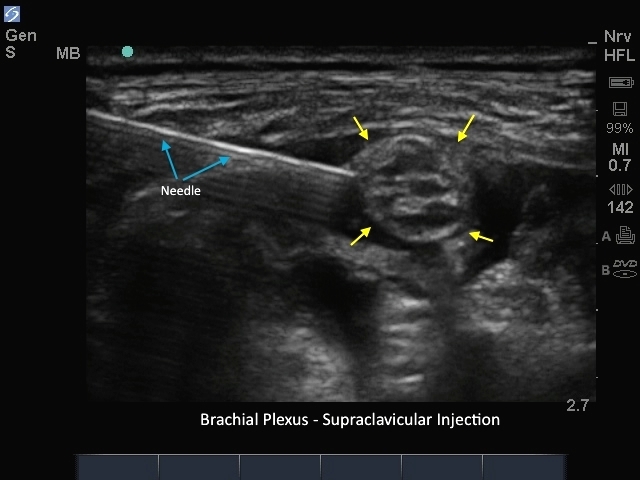
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular Injection
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular Injection
/sites/default/files/201410_Image_M-Turbo_Brachial_Plexus_Supraclavicular_Injection.jpg
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular nerve block.
Clinical Specialties
Media Library Type
Media Library Tag
Body
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Supraclavicular nerve block.
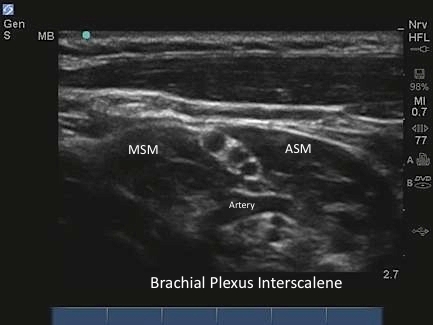
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level 5
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level 5
/sites/default/files/201410_Image_M-Turbo_Brachial_Plexus_Interscalene_Level_5.jpg
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level 5.
Clinical Specialties
Media Library Type
Media Library Tag
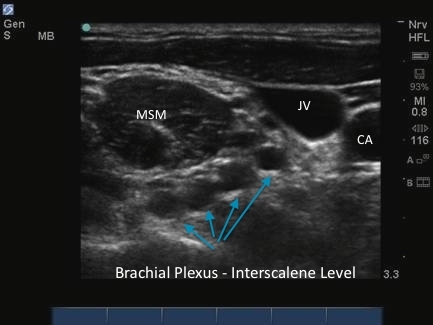
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level 4
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level 4
/sites/default/files/201410_Image_M-Turbo_Brachial_Plexus_Interscalene_Level_4.jpg
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level 4.
Clinical Specialties
Media Library Type
Media Library Tag
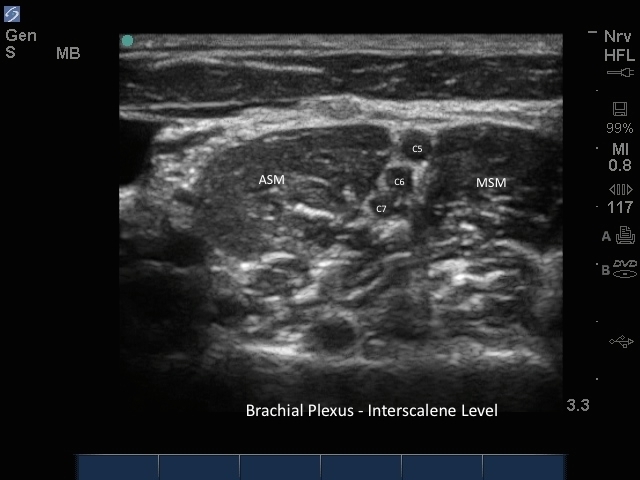
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level - 3
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level - 3
/sites/default/files/201410_Image_M-Turbo_Brachial_Plexus_Interscalene_Level_3.jpg
M-Turbo: Brachial Plexus Interscalene Level 3.
Clinical Specialties
Media Library Type
Media Library Tag

