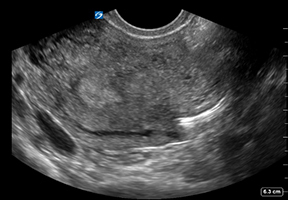
TV Uterus with Migrating IUD Transverse
TV Uterus with Migrating IUD Transverse
/sites/default/files/TV_Uterus_with_Migrating_IUD_Transverse.jpg
TV Uterus with Migrating IUD Transverse
Applications
Clinical Specialties
Publication Date
Media Library Type
Media Library Tag
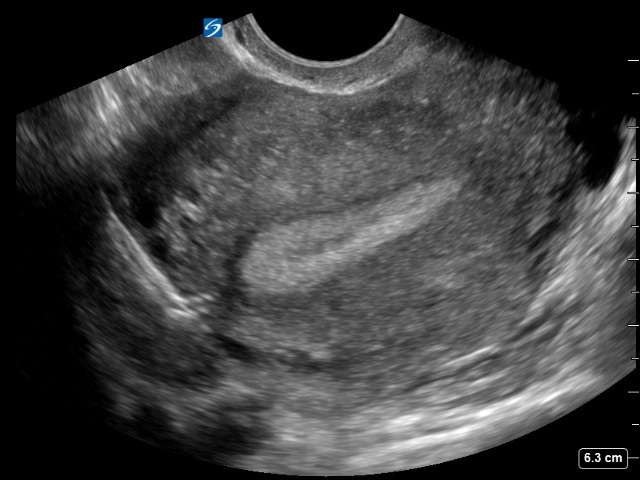
TV Uterus with Migrating IUD Sagittal
TV Uterus with Migrating IUD Sagittal
/sites/default/files/TV_Uterus_with_Migrating_IUD_Sagittal.jpg
TV Uterus with Migrating IUD Sagittal
Clinical Specialties
Publication Date
Media Library Type
Media Library Tag

